Neurological Disorders
Neurological disorders are diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system. In other words, the brain, spinal cord, cranial nerves, peripheral nerves, nerve roots, autonomic nervous system, neuromuscular junction, and muscles. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms.
What leads to Neurological Disorders?
- Genetic disorders
- Congenital abnormalities or disorders
- Bacterial (i.e. Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Neisseria meningitidis), Viral (i.e. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Enteroviruses, West Nile Virus, Zika), Fungal (i.e. Cryptococcus, Aspergillus), and P(i.e. malaria, Chagas) Infections
- Lifestyle or environmental health problems including malnutrition
- Brain injury
- Spinal cord injury
- Nerve injury.
Symptoms
- headaches
- numbness or loss of strength in a limb
- dizziness
- fainting and loss of consciousness
- memory problems
- cognitive difficulties
- speech problems
- vision problems
- tremors, spasms, and involuntary contractions
Some Major Neurological Disorders
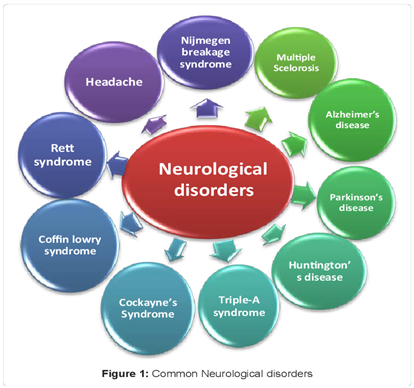
Some common neurological disorders include epilepsy, Alzheimer disease and other dementias, cerebrovascular diseases including stroke, migraine and other headache disorders, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, neuroinfections, epilepsy, autism, cerebral palsy, brain tumours, traumatic disorders of the nervous system due to head trauma, and neurological disorders as a result of malnutrition.
Regardless of the cause, all neurological disabilities result from damage to the nervous system. Depending on where the damage takes place, determines to what extent communication, vision, hearing, movement and cognition are impacted.
Diagnosis
Medical tests may vary depending on the affectation that the patient has. There are multiple tests to evaluate the state of the nervous system, which are more useful depending on what one wants to check. The following should be highlighted:
- Electroencephalogram: is especially useful in brain tumors or brain or spinal cord inflammation, for example.
- Cerebral angiography: used to locate vascular irregularities in the brain. They can be obstructions in the blood vessels or stroke, among others.
- Computed tomography: very effective in the detection of epilepsy, brain tumors or cysts, brain damage by injury, etc.
- Magnetic resonance: this reveals to the doctor the details of organs, tissues, nerves and bones.
- Lumbar puncture: to obtain samples of cerebrospinal fluid and thus check the existence of bleeding or cerebral hemorrhages.
Treatment & Management
In some cases it is possible to mitigate some symptoms with the following:
- Medication
- Lifestyle changes
- Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Surgery
Source: World Health Organization